Main Types of Solar Inverters – What Should you Choose?
Inverters convert direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC), which we use mainly at homes. Solar panels produce energy from sunlight in direct current, and the inverter converts direct current into alternating current, which powers electric appliances. So if you are considering a solar panels system, then you must start considering an inverter that makes the system efficient. Many people consider solar panel inverters as the brain of the solar panel system. In solar panels systems, inverters are the most important equipment after solar panels.
Inverters can monitor so the installer or owner, or maintainer can get knowledge about the performance of the system. Solar inverters provide information regarding problems. Your O&M crews can get help in identifying and fixing problems. Inverters also take responsibility for battery management. Today’s topic is the types of solar inverters. We will go over all of them to see what fits your needs.
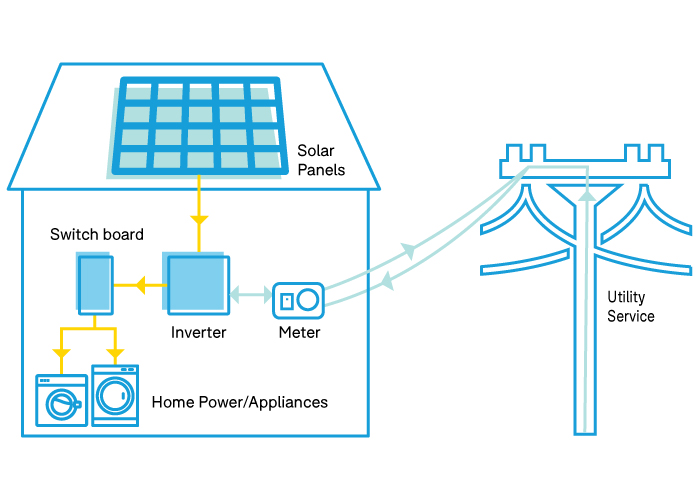
Types of Solar Inverters
Mainly three types of inverters are available for you in the market: string (centralized) inverter, power optimizer (string inverter + power optimizer) and Microinverters. String inverters are mainly used inverters in the world and comprise a majority. Power optimizers and microinverters combine called as Module-Level Power Electronics or MLPEs. They are gaining popularity at a rapid pace. Their prices have come down in markets. We know that string inverters are dominant, but it is found that people use MLPEs too in the US Microinverters and power optimizer systems are more expensive than string inverters.
String Inverters
A string inverter is used with solar arrays to convert direct current into alternating current. They are the most commonly used inverters in today’s time. It comprises a big part of the world’s inverter market. It is the most cost-effective inverter available for you. Generally, companies offer you this inverter if your roof is not shaded and panels do not face different directions.
These inverters are commonly used in residential areas for commercial purposes. There may be more than one string inverter present depending on the size of the installation. If a panel starts producing lesser power than others because of some reasons like shade, the other panels will start producing power to the suffering panel’s level. So sometimes it is not the best option available to you. It saves copper in DC cabling, because of a single serial connection.
- Cost Range: $1000 to $2000 depending on brand and size.
Power Optimizer
Power optimizer offers the same benefit as microinverter does. It is slightly cheaper than the microinverters. It reduces the impact of shading. Using a power optimizer with a system is more affordable than using a microinverter. It also provides panel performance monitoring at the same time. They are a compromise between string inverters and microinverters. Power optimizers do not convert DC into AC, they conditionalize DC and send it to the string inverter, which increases efficiency.
- Cost range: slightly lower than microinverters. Adding to a few panels costs only a few hundred dollars.
Central Inverters:
Central inverters are the same as string inverters, but they are bigger than them. We usually do not use them in residential areas for commercial purposes. They can handle up to 500KW per compound. So we use them in big buildings or installations. As solar panels are installed in a row connected to a string so central inverters can support more strings. You can call it a large string inverter. The advantage of having it is high efficiency. It is cheaper if we talk about per watt. The basic problems are its size and noise. A system can handle more power with it.
- Cost range: Around $0.4 per Watt peak
Microinverters
Microinverters are small inverters. They require separate installation along with each solar panel. Microinverters are becoming common day by day.
They can get more expensive than power optimizers and string inverters. Their costs are falling over time. It also allows you performance monitoring. Shades will not have that much of an impact on it because of individual connections. They are becoming popular for residential and commercial installations. It is quite safe. You can easily update and repairing old panels. But it costs expensive per watt in dollars. It increases the complexity of installation. Microinverters cost more maintenance costs as many inverters use to be in an array.
- Price range: Single microinverter can cost around $200. Speaking overall, it usually costs 20% more than using a string inverter.
Battery Inverters
Battery inverters manage the charging and discharging of the battery bank. They not only convert DC into AC but also convert AC into DC for charging battery bank from the solar panel system. These inverters retrofit batteries to your solar panel system or keep them separate. It converts battery power into 230V AC. With the growth of solar plus storage, battery inverters become important.
- Cost range: It typically adds $2000 – $3000 to the overall cost.
Hybrid Inverters
Hybrid inverters (aka multi-mode inverters) provides a mixture of on-grid and off-grid inverter solution. They allow you to plug or connect batteries into your solar power system. These inverters intervene in the battery by utilizing a technique called DC coupling. Hybrid inverters are a great value for the money. They provide a complete alternative to an off-grid solution, which saves you money each day usage because it is smart. They also capable of providing backup solutions during a power break.
- Cost range: Usually $1000 – $2000, but $3000 models are also available.
I know all the types of Solar Inverters, but which one is good for me?
It all depends on your needs. Check this list, because it tells the most prominent features and uses of each type of inverter.
- String Inverter is good for most homes, most commonly used, is less expensive. The only downside is if one panel becomes slow and less efficient, it can make the entire system less efficient.
- Battery Inverters is for connecting a battery to an existing system.
- Microinverters provide more flexibility and perform relatively well in partial shades. It can provide an efficiency increase of 12% overall.
- Hybrid Inverters need a compatible battery, which is more expensive than regular inverters, but prices are falling. They provide the best reliability.
- Power Optimizers are not exactly inverters but are added to an existing Solar PV system. They cost less than full microinverter installation, yet provide similar efficiency.
- All types of Solar Inverters need your attention because they are an important factor in the overall efficiency of the solar PV system.

I need information on Apex inverter